状态机
约 506 个字 39 行代码 18 张图片 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
1. 时序逻辑电路知识
1.1 同步时序逻辑电路分析

前置知识:触发器的特性方程:

例子:

-
CLK统一:同步时序逻辑电路
-
驱动方程:

下面进行描述:
- 状态转换表和状态转换图

需要标出时钟信号的顺序,上面的一行的Q1* 正好是上面的Q1
n个触发器正好有\(2^n\)个



\(Q_2 Q_1\) 在A的条件下,看Y
\(2^n\) 个 圆圈, \(2^{n+m}\)个箭头
设计方法
Step 1 逻辑抽象




例题:设计带有进位输出端的十三进制计数器
- 逻辑抽象:
- 13进制:13个状态
- 需要进位输出信号
- 默认加法计数器,是Moore型,不需要输入信号
- 十三个状态,4个触发器;
- 自然二进制的0000~1100,0-12来表实状态

- 状态转换图转换为基本方程组 -- 列成卡诺图的形式

理解:输出变量Q* 由输入变量Q和X决定



Verilog 写 FSM
教程: https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/verilog-fsm.html Problem 118 Simple FSM1 / Fsm1
牛刀小试
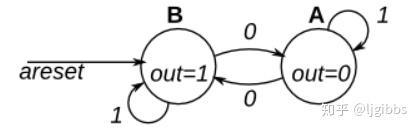
图中是一个有两个状态的摩尔型状态机。有一个输入信号与一个输出信号。本题中需要实现图中的状态机,注意复位后状态为 B,复位采用异步复位。
解答与分析
module top_module (
input clk,
input in,
input areset,
output out
);
// -----实现状态机
endmodule
这里我们学习标准答案中的表示,采用三段式的写法来描述这个简单的状态机。三段式状态机虽然代码会长一些,但能够更方便地修改,并更清晰地表达状态机的跳变与输出规则。
使用参数来表示每个状态。
// Give state names and assignments. I'm lazy, so I like to use decimal numbers.
// It doesn't really matter what assignment is used, as long as they're unique.
parameter A=0, B=1;
reg state; // Ensure state and next are big enough to hold the state encoding.
reg next;
// A finite state machine is usually coded in three parts:
// State transition logic
// State flip-flops
// Output logic
// It is sometimes possible to combine one or more of these blobs of code
// together, but be careful: Some blobs are combinational circuits, while some
// are clocked (DFFs).
三段式分别指
- 状态跳转逻辑
- 状态触发器实现
- 输出逻辑
状态跳转逻辑,根据输入信号以及当前状态确定状态的次态。
// Combinational always block for state transition logic. Given the current state and inputs,
// what should be next state be?
// Combinational always block: Use blocking assignments.
always@(*) begin
case (state)
A: next = in ? A : B;
B: next = in ? B : A;
endcase
end
状态触发器实现,在时钟边沿实现状态寄存器的跳变以及状态复位
// Edge-triggered always block (DFFs) for state flip-flops. Asynchronous reset.
always @(posedge clk, posedge areset) begin
if (areset) state <= B; // Reset to state B
else state <= next; // Otherwise, cause the state to transition
end
输出逻辑,根据当前状态实现输出
// Combinational output logic. In this problem, an assign statement is the simplest.
// In more complex circuits, a combinational always block may be more suitable.
assign out = (state==B);